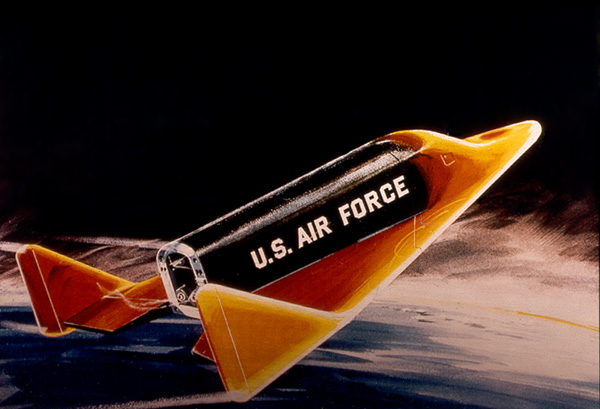
The Dyna-Soar, or “Dynamic Soarer,” officially known as the X-20 Dyna-Soar, was an ambitious spaceplane project developed by the United States Air Force during the 1950s and 1960s. Conceived during the early days of the space race, the Dyna-Soar was designed to perform various missions, including reconnaissance, satellite maintenance, and even bombing. The project aimed to create a reusable spacecraft capable of gliding back to Earth like an airplane, which was revolutionary at the time.
The Dyna-Soar was developed by Boeing and resembled a small, winged aircraft with heat-resistant materials to withstand the intense heat of re-entry into Earth’s atmosphere. It was designed to be launched atop a powerful booster rocket, like the Titan III, and then maneuver in space before returning to Earth. Unlike traditional capsules of the time, the Dyna-Soar’s design allowed it to land on a runway, giving it unique versatility.
Despite its innovative design, the Dyna-Soar faced numerous challenges, including technical difficulties, high costs, and a lack of a clear mission as NASA’s focus shifted towards manned lunar exploration. In 1963, after spending over $660 million on the project, the U.S. government canceled the Dyna-Soar, favoring other space endeavors such as the Gemini program.
Though it never flew, the Dyna-Soar was an important step in aerospace development. Its concept influenced later spaceplane designs, including the Space Shuttle, highlighting the early vision of reusable spacecraft that would come to shape the future of human spaceflight.
Document Archive
 Strangled Infant: The Boeing X-20A Dyna-Soar by Clarence Geiger, Date Unknown [214 Pages, 4MB]
Strangled Infant: The Boeing X-20A Dyna-Soar by Clarence Geiger, Date Unknown [214 Pages, 4MB]
 Loading...
Loading...